Balanced Scorecard
Elements of Balanced Scorecard:
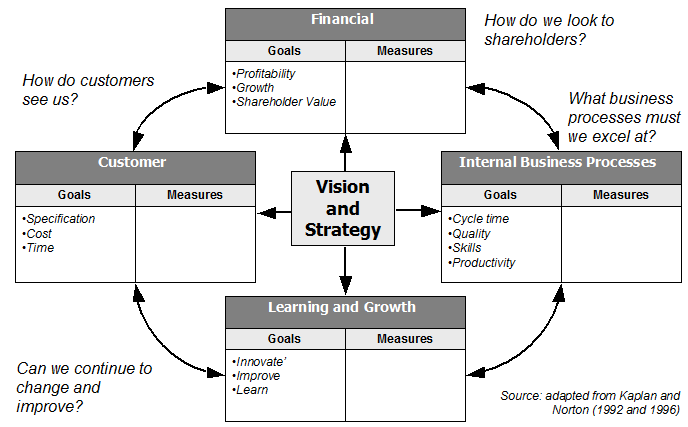
- Financial Perspective: This element focuses on financial metrics and objectives that indicate the financial health and performance of a business.
- Customer Perspective: This element considers metrics related to customer satisfaction, retention, and acquisition, reflecting the value the business provides to its customers.
- Internal Business Processes: This element examines the key processes and operations that are critical to delivering value to customers and achieving financial objectives.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: This element addresses the organization’s capacity for learning, innovation, and development of human and technological resources.
Principle:
Balancing financial objectives to critical success factors as process capabilities, customer satisfaction and learning/change.
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management framework designed to provide a balanced view of an organization’s performance. It emphasizes that business success is not solely determined by financial indicators, but also by factors like customer satisfaction, internal processes, and organizational growth.
Issues:
Kaplan & Norton, 2002 Five key areas of activity
- Translating vision and strategy into operational terms
- Aligning the organisation to strategy
- Making strategy everyone’s job
- Making strategy a continual process
- Mobilising change trough executive change
Not: quick fix, performance measurement, all organisations
Metric Selection: One challenge with the Balanced Scorecard is selecting the right metrics that truly align with the organization’s strategic objectives. Choosing inappropriate or irrelevant metrics can lead to misinterpretation and misguided decision-making.
Implementation Complexity: Successfully implementing a Balanced Scorecard requires commitment and effort from all levels of the organization. It can be complex and time-consuming to gather data, set targets, and align the entire organization around the framework.
Limitations and dangers: Demands management maturity and flexibility, demands participative management, to many measures, time and effort, potential flexibility lack, internal perspective
Interdependence between the 4 perspectives a strength
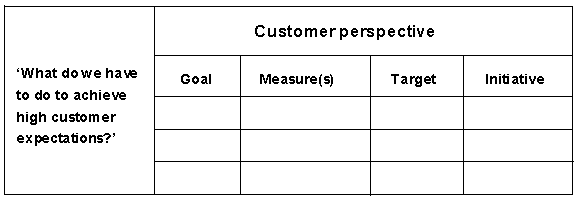
Setting up goals, measures, targets, initiatives (milestone targets throughout future years)
Customer perspective example:
Applications:
The Balanced Scorecard is used as a strategic planning and management tool. It helps organizations align their activities with their vision and strategy, monitor progress, and communicate performance across all levels of the organization.
- To secure a few key success measure that make change more likely
- To communicate vision, values and strategy to all in organisation
- To catalyse culture change
- As framework for business planning
- Provide KP measures against targets (benchmarks)
- Support decision-making by effect evaluation
- To provide feedback and learning
Source of Balanced Scorecard:
(Kaplan & Norton, 1992 & 1996)
The Balanced Scorecard framework was introduced by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in their Harvard Business Review article titled “The Balanced Scorecard – Measures that Drive Performance” (1992). Since then, numerous articles, books, and academic studies have explored and expanded upon the concept, providing both theoretical and practical insights into its application in various industries and organizational contexts