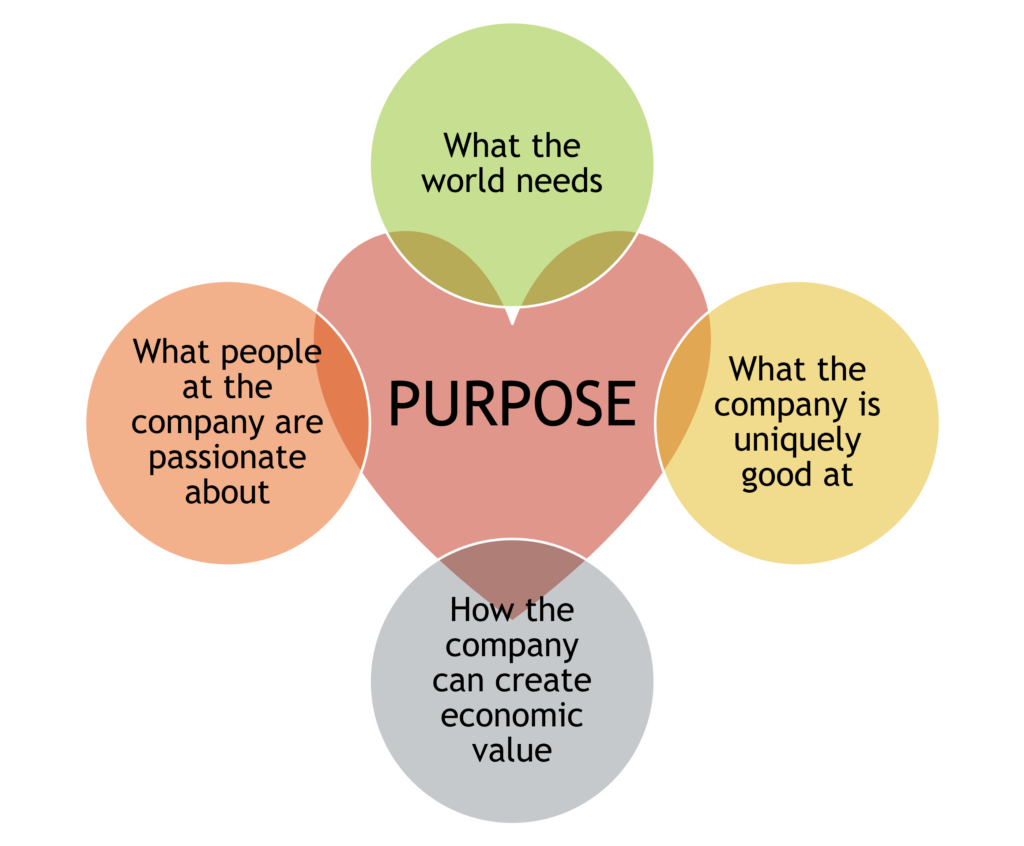
Elements of Purpose:
- What the world needs
- What the company is uniquely good at
- What people at the company are passionate about
- How the company can create economic value
Principle:
The “Purpose” model by Hubert Joly is guided by the principle that purpose-driven organizations are more successful and resilient in the long run. It emphasizes the importance of having a clear and meaningful purpose that inspires and motivates employees, attracts customers, and creates value for all stakeholders.
- Clarity of Purpose: The model emphasizes the importance of having a clear and compelling purpose that defines the organization’s reason for existence. This includes articulating the organization’s mission, vision, values, and long-term goals.
- Alignment with Stakeholder Needs: Purpose is not just about the organization’s internal goals but also about meeting the needs and expectations of its various stakeholders, including customers, employees, shareholders, and communities.
- Integration into Strategy: Purpose should be integrated into the organization’s strategic planning process, guiding decision-making and resource allocation to ensure that actions are aligned with the organization’s overarching purpose.
Issues:
- Defining Purpose: One challenge organizations face is defining their purpose in a way that is meaningful, authentic, and relevant to their stakeholders. Without a clear purpose, organizations may struggle to articulate their value proposition and differentiate themselves in the marketplace.
- Maintaining Alignment: Another challenge is maintaining alignment between purpose and strategy over time. As organizations evolve and face changing market conditions, they must continually reassess their purpose and ensure that their actions remain consistent with their stated values and goals.
- Measuring Impact: It can be difficult to measure the impact of purpose on organizational performance, making it challenging for leaders to justify investments in purpose-driven initiatives and to demonstrate the tangible benefits to stakeholders.
Applications:
- Strategic Planning: The Purpose model is applied in strategic planning processes to define the organization’s purpose and integrate it into its overall strategy.
- Organizational Culture: Purpose is used to shape organizational culture, values, and behavior, fostering a sense of meaning, belonging, and commitment among employees.
- Brand Building: Purpose-driven organizations use their purpose as a key differentiator and value proposition in building their brand and attracting customers.
Source:
Hubert Joly, the former CEO of Best Buy, outlined the Purpose model in his book “The Heart of Business: Leadership Principles for the Next Era of Capitalism.” (2021) While there may not be specific scientific sources dedicated to this model, Joly’s book and related articles provide insights into the role of purpose in driving organizational success and sustainability. Additionally, academic research in the fields of organizational behavior, leadership, and corporate social responsibility explores the impact of purpose-driven strategies on organizational performance and stakeholder engagement.