5.3 Strategy Implementation
The theoretical proposition resulted in development of a hypothesis that was to be tested by the research questions.
(2) Outcomes of strategic intent are heavily influenced by allocation of investments, resources and performance management practice.
The interdependence between strategic intent and outcomes is initially described based on the data collected.
The sub-chapters analyse and determine data relationships that answer the research questions.
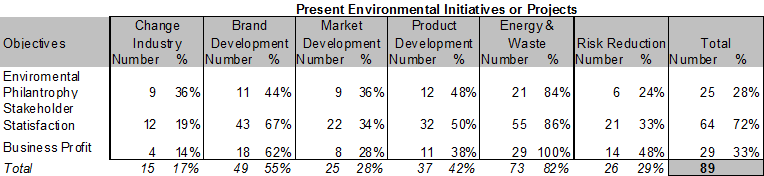
The respondents that have both responded positively on holding environmental objectives and present environmental initiatives or projects are included. This has excluded the 47 respondents mentioned in 5.2.
The top three out of six environmental initiatives and projects consist of energy and waste improvement (82%), brand & culture development (55%) and product development (42%).
Risk reduction (29%) and market development (28%) was selected in the bottom three with initiatives for changing the industry (17%) as the lowest.
Stakeholder satisfaction was stated to be the major objective (72%) compared to the present environmental initiatives and projects. Environmental business profit objectives (33%) and owners’ interest in environment (28%) achieved a lower rate.
Q7 multi choice / Q11 multi choice
Non respondents: 18 (-47 with no objective)
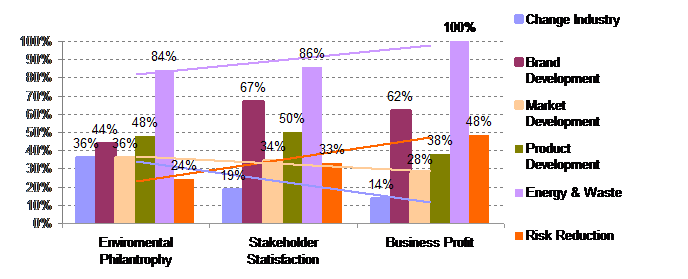
The general strong tendencies appear to be that respondents selecting environmental business profit objectives prioritize initiatives or projects mostly within energy & waste (100% – 84% span) and risk reduction (48% – 24% span) higher than others. Whereas initiatives for market development (36% – 28% span) and change of industry context (36% – 14% span) are prioritized lower.
Brand development (67% – 44% span) and product development (50% – 38% span) seems to be more fluctuating and independent of strategic intent rather than tendency related.
Research questions that tests the lead hypothesis are determined to be:
5.3.1 Key Success Factors
2 a) Do priorities of industry Key Success Factors strongly influence outcomes?
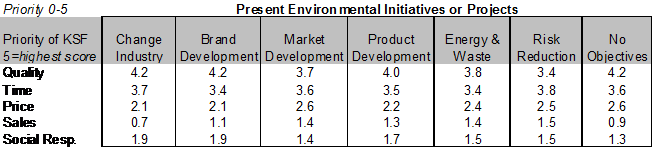
The interdependence between Key Success Factors and outcomes of strategic environmental objectives was analysed based on the data collected (multi choice selection) in the questionnaire and illustrated below.
Delivery of agreed quality was prioritised highest (3.9) followed closely by deli-very at agreed time (3.9). Delivering at the agreed price was prioritised in the middle (2.4). Social responsibility was prioritised second lowest (1.6) and sales and market share as the lowest (1.2).
Q4 priority / Q11 multi choice
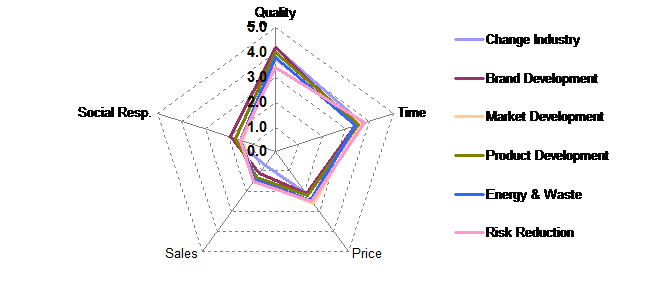
Respondents: 87 (47 with no objective)
Non respondents: 20
There does not appear to be strong differences between Key Success Factors and the present environmental initiatives or projects.
5.3.2 Present Capabilities
2 b) Do differences in the present capabilities strongly influence the outcomes?
The interdependence between the need for a tool box and environmental initiatives or projects was analysed based on the data collected (multi choice selection) in the questionnaire and illustrated below.
All respondents not having environmental objectives are compared and contrasted as well. 76% of those stated that a tool box would improve their ability to create value based on environmental improvements.
The majority of respondents having present environmental initiatives (range from 52% – 67%) stated they had sufficient tools. The need for capabilities seems to be there.
Q12 single choice / Q11 multi choice
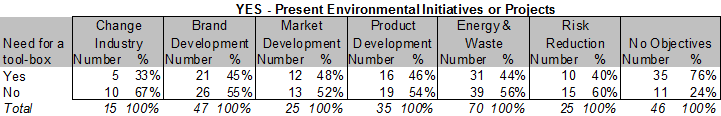
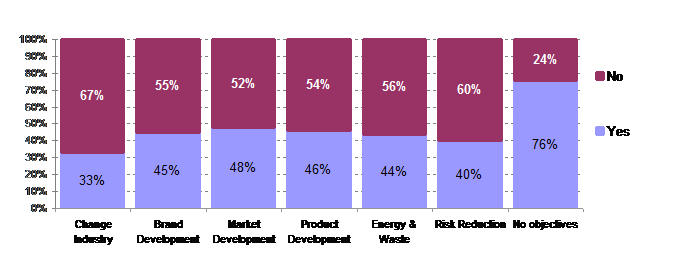
Non respondents: 28
However, analysing the data there seems to be no clear influence between the potential need for at tool box and environmental outcomes.
When linking the need for a tool box to other relationships in the data-output, an apparent issue is the relatedness to cooperative or competitive motives.
Q7 yes or no /Q12 single choice
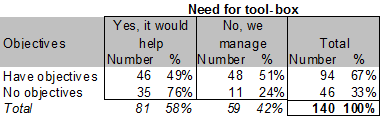
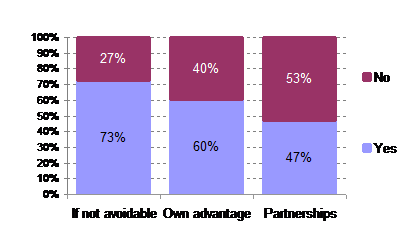
Non respondents: 31
73% of respondents that are only sharing knowledge and resources if not avoidable state the need for a tool box, and 53% of respondents sharing with partners do not.
It appears that if not cooperating with partners there is a greater need for capabilities.
5.3.3 Strategic Focus
2 c) Do differences in the strategic focus areas strongly influence outcomes?
The interdependence between focus on and environmental initiatives or projects was analysed based on the data collected (multi choice selection) in the questionnaire and illustrated below.
When comparing responses from respondents stating they have strategic objectives it can be seen that focus has no influence on the spread of initiatives or projects.
Q10 multi choice / Q11 multi choice
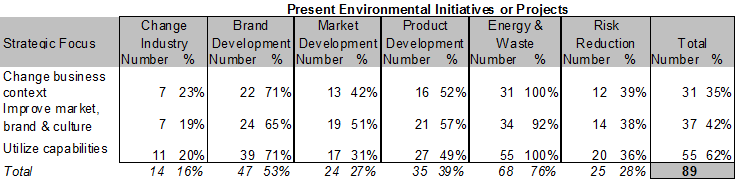
(47 with no objective)
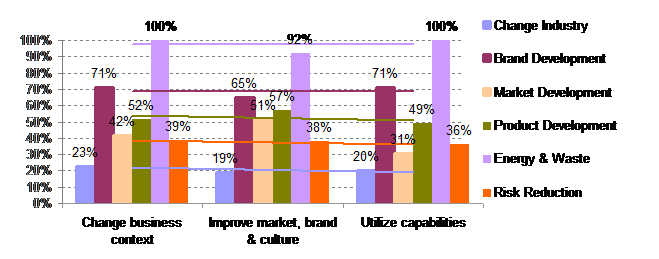
Non respondents: 28
There seems to be no relationship between strategic focus and outcomes of environmental initiatives.
5.3.4 Quality and Performance Management
2 d) Do differences in Quality and Performance Management strongly influence outcomes?
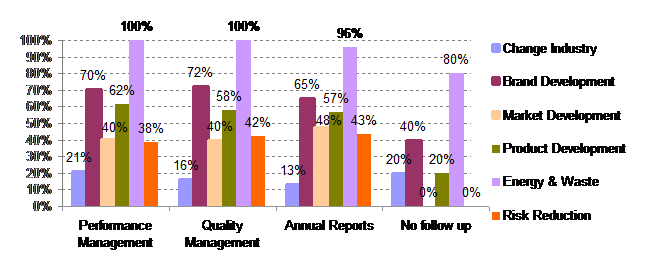
The interdependence between performance management reporting and initiatives in environmental improvements was analysed based on the data collected (multi choice) in the questionnaire and illustrated below.
Analysing the initiatives or projects followed up in performance management, quality management and/or annual reports, the top three are energy and waste (100% – 96%), brand development (72% – 65%) and product development (62% – 67%). The same three are the top three areas identified in 5.2.
There are only 5 (6%) respondents not following up on environmental initiatives, but there seems to be a lower level of initiatives and focus among those than the rest.
Q8 multi choice / Q11 multi choice
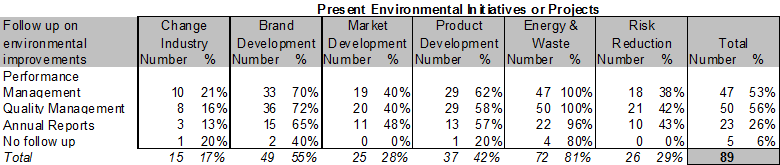
Non respondents: 18
It appears that management reporting influences the selection of environmental initiatives.