Ratio List – Profitability, Working Capital/Liquidity, Financial Structure/Investors Criteria, Corporate ratios
With reference to Pyramid of Ratios
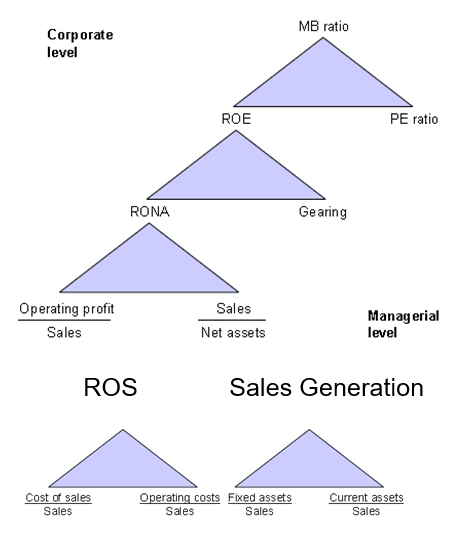
Elements of Financial business ratios:
Principle:
Lists financial business ratios with abbreviation, how to calculate, usefulness and major issues.
Issues:
Its important to related figures to seasonal fluctuations as these can affect the figures ass well as the organisations need for working capital (e.g. to sustain peek periods).
Basis
Source/quality of financial information
- External reports
- Internal reports
- Audited?
- Marketing coloured information e.g. via web sites
Regulatory framework
- Companies Act
- Accounting Standards
- Stock Exchange Regulation
- Other
- Changes during a period or compared to others?
Other/supplementary ways of financial analysis
Trend analysis
- However important to relate to assumptions, changes in major events and the trends of the environment, trends of market and competitors etc.
- Removes the absolute size of the figures making comparison easier
Dividends
- Stable dividends is a sign of strength
- Dividend has an information content (shows that the company is earning money)
- Shareholder do like cash income
- Maintenance of a steady dividend policy will maintain the share price
Applications:
Usefulness for management
Effective means to summarise detailed information (give overview)
Because the need to achieve a satisfactory liquidity position is vital for survival “customer is king – cash is god”.
The way that a companies total finances has been arranged is important to balance between various sources of funding including short and long term finance.
Internal view to evaluate performance of the company’s (managements) actions
- In relation to competitors
- In relation to past performance
To identify
- Changes
- Improvement possibilities
Usefulness for investors
To assist in investment decisions
External view to evaluate/benchmark performance of the company
- In relation to competitors
- In relation to past performance
To identify/evaluate
- Possible return on investment in the company
- The risk of the investment
- Compared to other companies and the market
(For lenders)
To identify
- Risks and the company’s ability to service its obligations)
Source of Financial business ratios:
Henley Business School