Elements Organisational Stages:
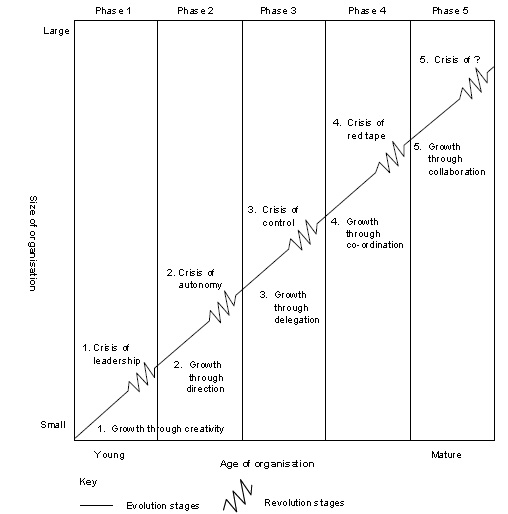
Growth Stages in relation to Organisational Size and Age
Principle:
Illustrate the series of crisis and growth, that influence leadership growth styles and leadership crises management in the different phases
| Category | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 |
| Management Style | Make and sell | Efficiency of operations | Expansion of market | Consolidation of organisation | Problem solving and innovation |
| Organisational Structure | Informal | Centralized and functional | Decentralised and geographical | Line staff and product groups | Matrix of team |
| Top Management Style | Individualistic and entreprenurial | Directive | Delegative | Watchdog | Participative |
| Control System | Market results | Standards and cost centres | Reports and profit centres | Plans and investment centres | Mutual goal setting |
| Management Reward | Ownership | Salary and merit increases | Individual bonus | Profit sharing and stock options | Team bonus |
| Phase 1 | Creative and informal management | Crisis of leadership – Growing organisation cannot be managed by informal methods alone |
| Phase 2 | Capable business management, more structure and formality | Crisis of autonomy – Demands for greater autonomy by lower-level managers |
| Phase 3 | Delegation and decentralisation | Crisis of control – Loss of control over diversified operations, parochial attitudes |
| Phase 4 | Greater coordination, systems and planning | Crisis of red tape – Procedures take presedent over problem-solving. Tension between line and staff |
| Phase 5 | Strong interpersonal collaboration, greater spontaneity in management | Crisis of ? – Employee burnout – need for revitalisation team problem-solving |
Issues:
Limitation of size within each phase
Length of phase dependent of industry growth rate
Today’s solution tomorrows problem
“Strategy drives structure”, Chandler (1962)
Organisational architecture as an important source of resource based advantage – Kay (1993)
Key initiatives might be:
Structual change and redesign, creation of networks, removal of bureaucracy
Attempts to create a “learning organization”
Reorganisation around core capabilities and “outsourcing” of others
New motivation and reward structures
Redesign career paths and novel human resource management principles
Leadership styles in phases:
Phase 1 Creative and informal management
Phase 2 Capable business management, more structure and formality
Phase 3 Delegation and decentralization
Phase 4 Greater coordination, systems and planning
Phase 5 Strong interpersonal collaboration, greater spontaneity in management
Applications:
To determine the organisations growth phase and appropriate leadership style and identify present stage to anticipate future challenges
Source Organisational Stages:
Evolution and revolution of organisations, (Larry E Greiner, 1972)