Stakeholder Power Interest & Circle
Elements of Stakeholder Power Interest & Circle:
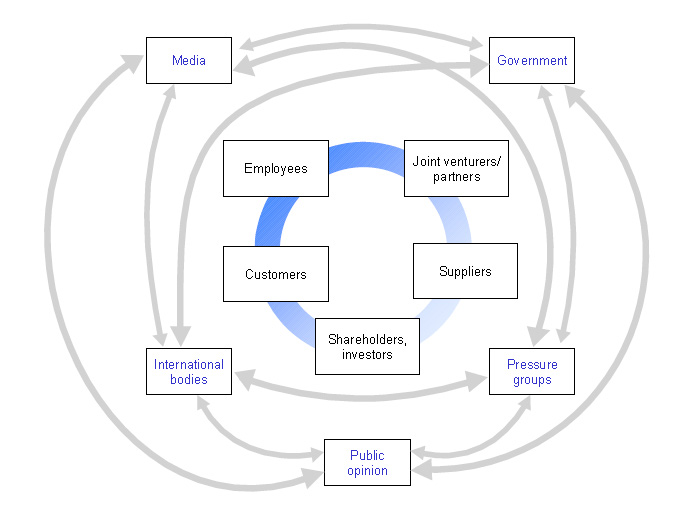
Circle Elements: Inner circle = direct exchange & Outer circle = indirect influence
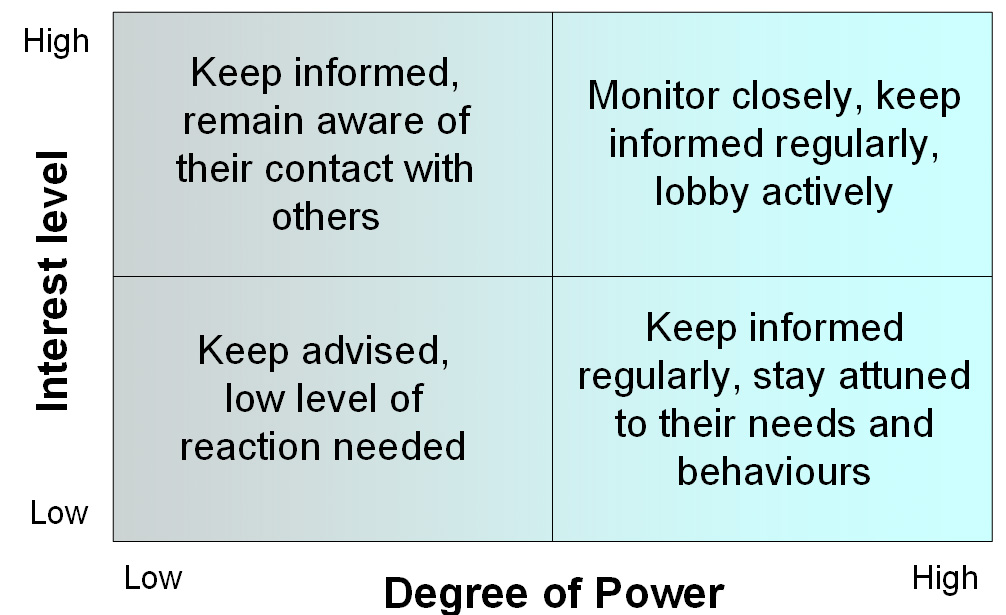
Matrix Elements: Action to be taken in relation to Power and Interest
Principle:
Mapping the stakeholders to determine strategies to use
Issues:
Social responsibility vs duty of a business man – Business ethics do not exist “per se” as human activity is governed by moral principles etc
Investment in society just as in R&D or marketing
Conflicting interest among stakeholders
Who the key blockers and facilitators of change are likely to be, and therefore, whether strategies need to be pursued to reposition certain stakeholders
which maintenance activities will be needed to discourage stakeholders from repositioning themselves
Hierarchy provides people with formal power
Exercising discretion is a most significant source of power
Influence can be an important source of power and may arise from personal qualities (of leadership) or because a high level of consensus exists within the group or company
Control of strategic resources is a major source of power within companies
specialist knowledge or skills
Control of the environment is another source of power within organisations
The most difficult group to cope with are those in segment D, since they are in a powerful position to block or support new strategies, but their ‘stance’ is difficult to predict
means must be found to ‘test out’ new strategies with these stakeholders before an irrevocable position emerges
Applications:
To determine who to be responsible to
Power of stakeholders need to be assessed
indicates the type of relationship which the organisation will need to establish with each stakeholder group
This is a useful way of accessing where the ‘political efforts’ should be channelled during the development of new strategies.
Source of Stakeholder Power Interest & Circle:
Mendelow’s Power-interest grid (Aubrey L. Mendelow, Kent State University, Ohio 1991)
(Cited in Scholes,1998)