Elements Lifecycle – Industry:
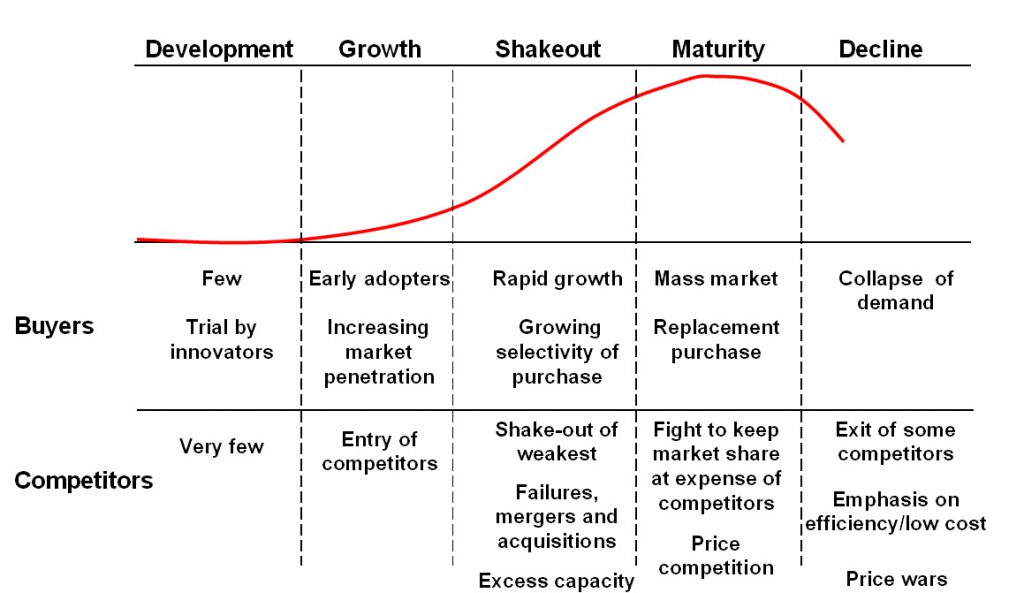
Buyer, competitor and internal needs compared to Industry lifecycle.
Relevant to map product or company portfolio to different lifecycle stages.
Principle:
Emerging industry characteristics:
- Strong technological uncertainty (absence of dominant design – Abernathy, 1975 – Wiki)
- Strategic uncertainty
- High Initial costs, but steep cost reduction
- Many embryonic companies and spin-offs
- First-time, badly informed buyers
- State intervention (subsidy)
Embryonic (mature with fundamental change)
- Rapid growth
- Changes in technology
- Great pursuit of new customers
- Fragmented and changing shares of market
Growth Industries
- Widening buyer group
- Consumer will accept uneven quality
- Products have technical and performance differentiation
- Reliability is the key for complex products
- There is continuous competitive product improvement
- Search for good quality
- Hig advertising, but lower percentage of sales than in the introductory phase, advertising and distribution are the key for non-technical products
- Under-capacity in manufacturing
- Shift towards mass production
- Use of mass channels
- Competition is through new entrants creating many competitors
- Mergers and takeovers are prevalent and some firms will be casualties
- Risks can be taken because growth conceals them
- Major strategic thrust is to grow faster than your competitors
Mature industries (Porter, 1980)
- Slowing growth means more competition for market share
- Firms in the industry increasingly are selling to experienced repeat buyers
- There is a problem in adding to industry capacity or personnel
- Manufacturing, marketing, distribution, selling and research methods are often changing
- New products and applications are harder to come by
- International competition increases
- Industry profits fall during the transition period, sometimes temporarily and sometimes permanently
- Dealers’ margin fall, but their power increases
Issues:
Emerging – set industry rules by:
- Product policy
- Marketing approach
- Pricing strategy
Embryonic – Largest strategic benefit (Porter)
- Shaping industry structure
- Balancing industry versus firm interests
- Changing roles of suppliers and channels
- Shifting mobility barriers
- Timing entry
Applications:
Insight in future profitability, cash-flow, marketing, competition
1: To determine approach according to life stage
2: Provide overview of portfolio – Competitive situation is addressed by SWOT analysis – indicates following lifestage/future trends to be expected
Source Lifecycle – Industry:
Henley Business School – Learning Resources