Elements of Types of Strategic Change:
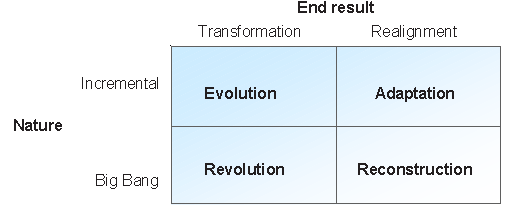
End result: transformation or Realignment
Nature: Incremental or BigBang
Results in:
Adaptation – Change which can be accommodated with the current paradigm (central beleifs and assumptions) and occurs incrementally through staged iniciatives aimed at realigning the way the organisation operates
Reconstruction – Change whocch may be rapid and could involve a good deal of upheaval in an organisation (e.g. major structural changes or cust-cutting programmes), but which does not fundamentally change the paradigm. They are about making organisations more efficient, or better at whetever they already do
Evolution – is transformational change implemented gradually through different stages and interrelated initiatives. It can be planned or forced transformation but can also occur in an emergent manner
Revolution – is fundamental, transformational change that occurs by useing simultaneous initiatives on many fronts, and often in a relatively short space of time. It is more likely to be a forced, reactive transformation(sometimes referred to as “chrisis management”)
Principle:
Shows relationship between end result and nature of change
Issues:
(Johnson & Scholes, 2002)
Bourgeois & Brodwin (1984) Five approaches:
- Leader strategy managers implement
- Leader strategy and implementation process (top down)
- Leader and manager share strategy and implementation
- Leader mission manager functional strategies
- Leader strategy evaluation framework manager ideas
Degree of risk: Predictability – commitment – ease of reversal
“Sometimes what appears to be a poorly judged choise can be turned around with appropriate changes during the implementation phase. It follows, therefore, that risk is best managed in an organisation that has a culture of flexibility and innovation and is succesful at getting its people involved and committed”
(Thompson & Martin, 2005)
Applications:
Applications: to determine how to manage change – which path to take
Source of Types of Strategic Change:
Balogun et al (2015)