Elements of The Distruptive Innovation Model:
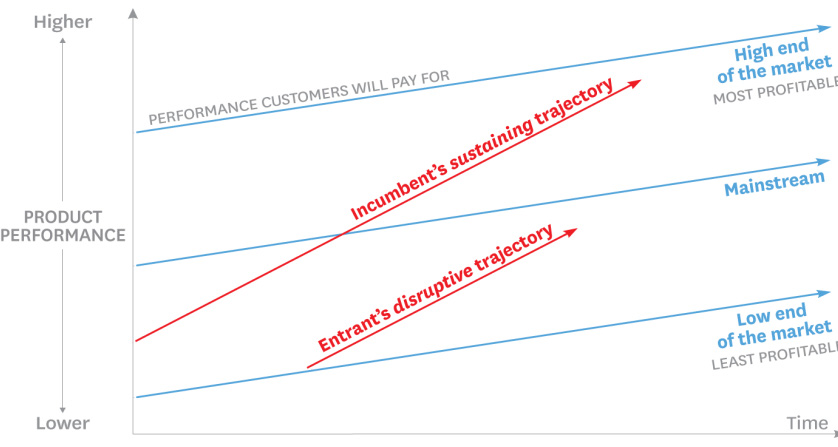
Relationship between level of product performance developed in an industry over time and the performance levels different customer levels are willing to pay for.
The RED lines showing how products or services improve over time
The blue lines showing customers’ willingness to pay for performance
Principle:
The model contrasts product performance trajectories (red lines) with customer demand trajectories (blue lines).
As existing companies tend to introduce high-quality products or services to compete in satisfying the high end market, where profitability is high, they overshoot the low-end customers demand. This leaves an opening for industry entrants or substituting low cost products or services.
Disruptive businesses enter the industry by offering low-cost products or services and the improve performance to enter their high profit market while satisfying the mainstream market.
Issues:
New product and services disruption vs exisiting product and services disruption – Development Strategies
New technology influence on marketing, sales and distribution cost
Disruptive business models
Bypassing the industry Value Network
The need for product development to grow the disruptive business into the profitable mainstream market
Fighting low-cost brands from existing industry businesses
Applications:
To assist in strategy selection and determine if disruptive strategies are relevant to an existing business or a startup business
Source of The Distruptive Innovation Model:
Christensen (2016)