5.2.3 Levels of Internationalisation
1 c) Do different levels of internationalisation strongly influence strategic intent?
The interdependence between internationalisation and objectives in environmental improvements was analysed based on the data collected in the questionnaire and illustrated below.
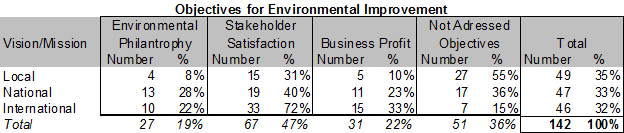
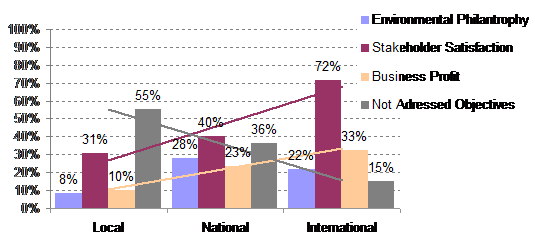
Level of internationalisation was evenly spread between local (35%), national (33%) and international (32%) respondents.
The strongest tendency appearing is the 72% of international respondents having objectives for environmental improvements to achieve stakeholder satisfaction compared to the 31% of local respondents.
Secondly, the tendency of 55% of local respondents that answered they had no environmental objectives compared to the 15% of international respondents.
Addressing business profit objectives also seems to increase from local (10%) to international (33%) respondents.
Q1 single choise / Q7 multi choise
Non respondents: 12
The interdependence indicated is that international companies are more likely to address environmental objectives for stakeholder satisfaction.
Formal statistical analysis is applied as the international interdependence appears crucial to the conclusions and the data structure supporting it allows for statistical testing.
The focus of statistical analysis will be narrowed down to a hypothesis where p1, p2 and p3 represent the proportions of the respondents for local, national and international businesses having stakeholder satisfaction as part of their environmental objectives:
H0: p1=p2=p3
Statistical conditions and calculations (chi-square and confidence intervals) can be found in appendix 6 based on the recommendations I Brymann & Bell (2007 p360)
The chi-square analysis rejects hypothesis H0 and confirms the significance (p-value = 0.00017) of the proportions, and relates the statistical characteristics to international businesses.
Resulting confidence intervals shows a rather big uncertainty (standard deviations 6.7% for international and 4.9% for national and local businesses) in estimating the proportions.
5.2.4 Position in Value Network
1 d) Do positions in the value network strongly influence strategic intent?
The interdependence between position in the value network (see figure 1 in 1.1.2) and objectives in environmental improvements when addressing stakeholders was analysed based on the pre segmentation and illustrated below.
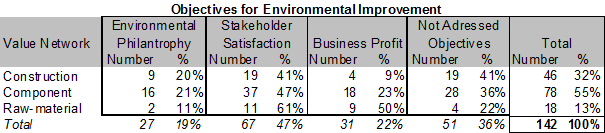
The component group accounted for 55% of the respondents and the construction group for 32% while the raw-material group was the smallest (13%).
The strongest tendency appears to be the difference between construction groups’ selection of profit related objectives (9%) compared to the raw-material groups’ (50%) selection rate, with the component group positioned in between (23%).
Secondly, the tendency of 41% of construction respondents that answered they had no environmental objectives compared to the 22% of raw-material respondents.
Also the level of stakeholder satisfaction objectives seems to increase from construction (41%) to raw-material (61%).
Pre-segmentation / Q7 multi choice
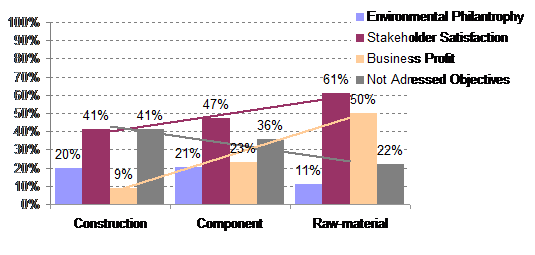
Non respondents: 12
In the data composition (5.1) it was determined that the raw-material group was the most international (58%), and the construction group the most local (62%). The levels of internationalisation (5.2.3) seem to influence the tendencies in the vale network groups, as the three tendencies determined under levels of internationalisation appear to be somewhat comparative.
The most distinct difference in objectives related to internationalisation seems to be the level of raw-material respondents (50%) selecting business profit related objectives, compared to the 33% of international respondents (see 5.2.3).
The interdependence thus indicated is that the further away from the consumer in the value network, the more likely companies are to address business profit objectives in environmental improvements.
5.2.5 Generic Competitive Strategies
1 e) Do different generic competitive strategies strongly influence strategic intent?
The interdependence between internationalisation and objectives in environmental improvements when addressing stakeholders was analysed based on the data collected (single choice selection) in the questionnaire and illustrated below.
69% responded they offer a broad pallet of products and 31% that they focus on special niche products.
53% responded they differentiated from competitors and 47% that they compete on low cost.
The strongest tendency appears to be that niche differentiators avoid selecting business profit related objectives (7%) compared to the other group’s selection rate (20% – 27%).
However it can be discussed if there is sufficient significance and statistical background to determine relatedness.
Q5 single choice / Q7 multi choice
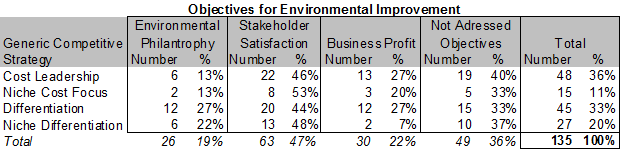
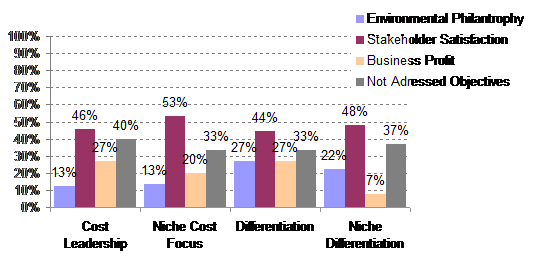
Non respondents: 19
It appears that generic competitive strategy holds no strong influence on objectives for environmental improvements for the industry.
5.2.6 Competence Utilization
1 f) Do different levels of competence utilization strongly influence strategic intent?
The interdependence between competence utilisation and objectives in environmental improvements when addressing stakeholders was analysed based on the data collected (multi choice selection) in the questionnaire and illustrated below.
Only tendency appears to be that utilisation of compliance to minimum requirements is less related to stakeholder satisfaction objectives (10-16% interval).
Q9 multi choice / Q7 multi choice
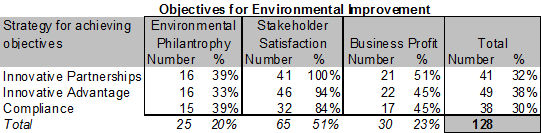
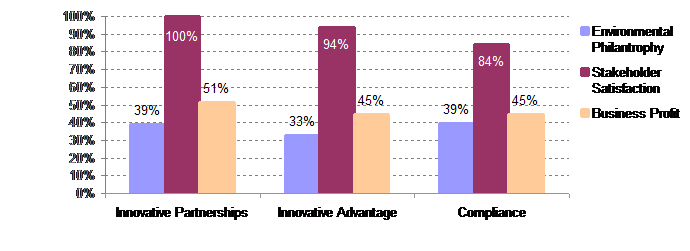
Non respondents: 19
It appears that competence utilisation holds no strong influence on objectives for environmental improvements for the industry.